A fully automated data warehouse for business intelligence.
Background
A critical inefficiency hindered the client’s operations: four senior executives were relied upon to manually gather business KPIs for invoicing, costing valuable senior leadership each 5-10 hours per week. This manual process not only wasted resources at the highest levels but also prevented executives from focusing on strategic initiatives.
Solution
To address this bottleneck and establish a scalable foundation for future Business Intelligence capabilities, I developed an automated BI platform featuring fully automated data pipelines and a highly scalable data warehouse.
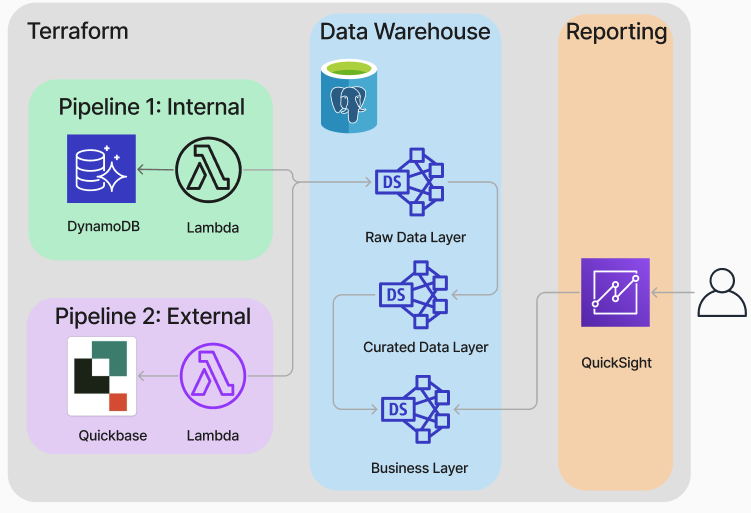
Data Warehouse Architecture
To align with the client’s existing cloud infrastructure, I prioritized leveraging AWS services for this project. For data pipelines, I chose AWS Lambda functions. Their serverless architecture inherently provides horizontal scalability and cost-efficiency, ideal for handling potentially variable data ingestion workloads.
To ensure robust and manageable data flow, AWS Step Functions were implemented for workflow orchestration, enabling reliable, and auditable ETL processes.
The data warehouse was built using AWS RDS PostgreSQL. PostgreSQL offered a performant and robust relational database engine, well-suited for BI workloads and capable of both vertical and horizontal scaling to accommodate future data growth and query demands. The data model leveraged the medallion architecture, ensuring efficient data organization and query performance.
Finally, infrastructure deployment was automated with Terraform. This Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) approach ensured repeatable, version-controlled, and consistent deployments across different environments, promoting maintainability and reducing deployment risks.
Governance and Security
Given the client’s requirement to adhere to stringent HIPAA and SOC regulations, robust data governance and security were paramount throughout the project lifecycle. To ensure compliance and data protection, I implemented a multi-faceted approach encompassing both technical controls and procedural policies. Access to sensitive data was rigorously controlled through IP whitelisting and Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), limiting access to authorized personnel based on the principle of least privilege. A standardized access request and approval process was established and documented for auditability. Data encryption was implemented both at-rest and in-transit. At-rest encryption was enabled using AWS RDS encryption. In-transit encryption was enforced utilizing TLS and SSL protocols to protect data confidentiality and ensure data integrity during transmission, crucial for meeting HIPAA and SOC requirements.
Logging and Monitoring
To maintain a robust security posture and ensure adherence to HIPAA and SOC regulations, comprehensive logging and monitoring were implemented across the entire BI platform. This included:
-
Data Pipelines: Detailed logging was enabled for all pipeline executions, capturing key metrics such as start and end times, data volume processed, success/failure status, and error messages. This allowed for proactive performance monitoring, troubleshooting, and data lineage tracking.
-
Data Warehouse: Database audit logging was configured within AWS RDS PostgreSQL to capture all data access and modification events, including user logins, queries executed, and schema changes. This provided a complete audit trail for security and compliance purposes.
-
Centralized Logging and Monitoring: Logs from all components were aggregated and centralized using AWS CloudWatch Logs, enabling efficient searching, analysis, and alerting.
-
Real-time Monitoring and Alerting (Prepared for Implementation): Dashboard designs were prepared and infrastructure was established to visualize KPIs and system health metrics in real-time. Automated alerts were prepared for configuration to trigger notifications for critical events, such as pipeline failures, security anomalies, or performance degradation, enabling rapid incident response. Due to project time constraints, full dashboard implementation and alert activation were prepared for future deployment by the client.
Automation Highlights & Code Showcase
Automation was central to the design of this BI platform, aimed at streamlining data workflows, infrastructure deployment, and operational monitoring for maximum efficiency and scalability.
Data Pipeline Automation
Data pipeline automation was crucial for ensuring timely and consistent data ingestion and transformation for invoicing. AWS Lambda functions were leveraged to create event-driven, serverless pipelines, eliminating manual data processing steps.
# Python Lambda function snippet for automated data ingestion
import sys
import pandas as pd
from api_handler import make_api_call
from database_handler import insert_data_into_table, get_db_connection
def main():
# Extract data from API
report_data = make_api_call(REPORT_DATA_URL, method='post')
if report_data is None:
print("Error fetching data. Exiting.")
sys.exit(1)
data_rows = report_data['data']
source_row_count = len(data_rows)
requests_df = pd.DataFrame(data_rows)
requests_data = requests_df.to_dict(orient='records')
# Connect to database
conn = get_db_connection()
try:
# Insert data
insert_data_into_table(conn, "verifyplus", ["...", "..."], requests_data) # Simplified headers
# Basic Row Count Validation
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute(f"SELECT COUNT(*) FROM raw.verifyplus")
inserted_row_count = cursor.fetchone()[0]
if inserted_row_count != source_row_count:
conn.rollback()
raise ValueError("Row count mismatch after insertion.")
conn.commit()
print(f"Successfully inserted {inserted_row_count} rows.")
except Exception as e: # Basic exception handling
conn.rollback()
print(f"Error during database operation: {e}. Rolling back.")
sys.exit(1)
finally:
conn.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Infrastructure Automation
Infrastructure deployment was fully automated using Terraform, enabling Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) principles. This ensured repeatable, consistent, and version-controlled infrastructure provisioning across different environments, significantly reducing manual configuration and deployment time.
# Terraform snippet for automated RDS PostgreSQL instance creation
resource "aws_db_instance" "itc_postgres_instance" {
identifier = var.db_identifier
engine = "postgres"
engine_version = "16.3"
instance_class = "db.t4g.micro"
allocated_storage = 20
storage_type = "gp2"
publicly_accessible = true
multi_az = false
username = var.db_username
password = random_password.db_password.result
skip_final_snapshot = true
deletion_protection = false
parameter_group_name = aws_db_parameter_group.itc_postgres_parameter_group.name
vpc_security_group_ids = [var.security_group_id]
db_subnet_group_name = aws_db_subnet_group.itc_db_subnet_group.name
tags = {
Name = var.db_identifier
}
}
Explore the Full Code on GitHub
For a comprehensive look at the project’s implementation details, including all automation scripts, data pipeline code, infrastructure-as-code configurations, and more, please visit GitHub for the full code repository.
